Condoms
Condoms protect you and your partner/s from unintended pregnancy. They also prevent sexually transmissible infections (STIs) – infections that can be passed on from one person to another during sexual activity, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea and HIV.
There are two types of condoms – external condoms (that go over a penis) and internal condoms (that go inside a vagina).
External condoms (that go over a penis)
The external condom is the only contraceptive currently available for people with penises.
It is made of thin rubber (latex) and is fitted over an erect (hard) penis. The condom collects the sperm and stops them entering a vagina, preventing them from meeting with an egg which may form a pregnancy.
Things to consider
- The condom must be rolled onto the penis before there is any close physical contact with a vagina.
- The condom must be taken off straight after the person with the penis ejaculates (cums).
- Take care when removing the penis from the vagina, mouth or anus otherwise the condom might come off or tear.
- Condoms are small and easy to carry.
- Condoms are can be purchased from pharmacies, supermarkets and through mail order at low cost.
- Condoms are available for free from some places (external site).
- When used correctly condoms are very effective at preventing pregnancy and STIs.
- Condoms can be used with other contraceptives (e.g. Implanon, IUD) for increased protection against pregnancy.
- Old condoms can break down - check the expiry date on the packet before use.
- Some people have an allergy to latex (rubber). You can get latex-free (polyurethane) condoms but they’re harder to find and more expensive.
- Oil-based lubricants can damage condoms. Water-based lubricants help stop the condom breaking – never use oil-based lubricants as they can damage the latex.
- Condoms also decrease the chance of most STIs. STIs can also be spread by oral or anal sex, so condoms need to be put on the penis before there is any close contact with a mouth or anus for it to be effective in preventing STIs.
- Condoms act as a barrier to STIs such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea and HIV.
- Condoms are less effective as a barrier to STIs that are spread through skin-to-skin contact (e.g. herpes, genital warts) because they only protect the skin that is covered.
How to use them correctly
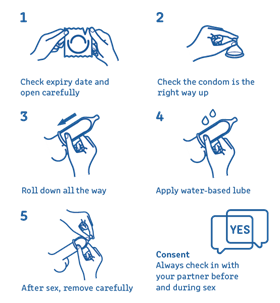 Check the expiry date.
Check the expiry date. - Open the packet carefully (don’t use teeth or scissors).
- Check the condom is the right way up – it should roll down easily.
- Squeeze the tip.
- Place over the tip of the erect (hard) penis.
- Roll all the way down to the base of the penis.
- Put water-based lube on the outside of the condom.
- Leave the condom on during sex.
- After sex, before the penis goes soft, hold the condom while pulling the penis out.
- Slide the condom off carefully to make sure the ejaculate (cum) stays inside the condom.
- Wrap the condom in a tissue and throw in the bin (not the toilet).
- You need to use a new condom each time you have sex.
Internal condoms (that go inside a vagina).
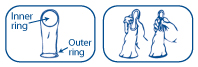
The internal condom is a polyurethane (plastic) pouch that fits inside a vagina. It has a soft ring on each end. The outer ring stays on the outside of the vagina and partly covers the labia (lips), while the inner ring fits on the inside of the vagina near the cervix to hold the condom in place. It collects the ejaculate, stopping the sperm from entering the vagina.
Things to consider
- A new internal condom must be used each time you have sex.
- It must be in place before any close physical contact with a penis takes place.
- It very effective at preventing pregnancy if used properly.
- The person wearing the internal condom has control over contraception.
- Internal condoms are small and easy to carry.
- Internal condoms fit all vaginas and can be used during your period.
- There are no problems with latex allergies (as they are made from plastic). This means you can also use oil-based lubricants.
- You don’t have to see a doctor.
- Internal condoms are sold at some health services and through mail order; they are not available from supermarkets or pharmacies.
- They are more expensive than external condoms.
- It can be inserted several hours before sex. This can help it warm to the body.
- The penis does not have to be withdrawn straight after ejaculation (cumming).
- It is possible for the penis to slip into the vagina between the internal condom and the vaginal wall.
- The internal condom can make a slight rustling noise during use. Lubricant can help prevent this.
- Take care when removing the penis from the vagina, otherwise the internal condom might come out or tear.
- Internal condoms offer protection against STIs such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea and HIV. Herpes and genital warts are spread through skin-to-skin contact, so condoms only protect the skin that is covered.
- If you have a new sex partner, or if you or your partner have sex with other people, use condoms to help prevent STIs. Use them in addition to any other contraceptive you may be using to increase protection.
How to use them correctly
- Check the expiry date and open carefully.
- The internal condom has a flexible ring at each end. The outer ring at the open end covers the area around the opening of the vagina. The inner ring is used for insertion and holding it in place. Rub the sides of the condom together to spread the lubricant.
- Hold the inner ring between your thumb and middle finger.
- Put your index finger on the pouch between your thumb and other fingers and squeeze the inner ring.
- Slide it into your vagina as far as it will go, pushing up the front of the inner ring so it slips into place. When it’s in the right place you can’t feel it. It can’t go in too far and it shouldn’t hurt.
- Make sure it is in the correct place and is not twisted. The outer ring should be outside the vagina.
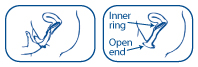
- If the female condom bunches up when the penis is inserted, stop, put on more lubricant, and guide the penis back in.

- After sex, remove the female condom before you stand up. Squeeze the outer ring and twist it, and pull it out gently.
- Wrap it in toilet paper, and put it in the rubbish bin, not down the toilet.
- Don’t re-use the internal condom.
Last reviewed: 03-11-2025
Acknowledgements
Sexual Health and Blood-borne Virus Program, Public Health
This publication is provided for education and information purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical care. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not imply endorsement and is not intended to replace advice from your healthcare professional. Readers should note that over time currency and completeness of the information may change. All users should seek advice from a qualified healthcare professional for a diagnosis and answers to their medical questions.